What is ISO/SAE 21434?
The ISO/SAE 21434 standard for Road Vehicles—Cybersecurity Engineering delineates responsibilities across different stages of automotive product development. It mandates executive management commitment to cybersecurity engineering throughout the product development process. The standard establishes consistent roles and responsibilities between vendors or suppliers and subsequent entities in supply chains, promoting uniform terminology industry-wide. It outlines clear objectives and outcomes for each phase of the product lifecycle, which inform subsequent stages. ISO/SAE 21434 includes Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) to evaluate cybersecurity risks in automotive products.
The ISO/SAE 21434 standard does not focus on the safety of an organization but on the safety of the vehicle occupants. The most important part of the ISO/SAE assessment is the correctly conducted Threat Analysis Risk Assessment (TARA).

ISO/SAE 21434 Standard
-
The ISO/SAE 21434 standard can be divided into 3 important parts:
- Organizational clauses:
- Organizational cybersecurity management.
- Distributed cybersecurity activities.
- Continual cybersecurity activities.
- Product lifecycle related clauses:
- Project dependent cybersecurity management
- Concept
- Product development
- Cybersecurity validation
- Production
- Operation and maintenance
- End of cybersecurity support and decommissioning
- Threat analysis and risk assessment methods
Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA)
As mentioned earlier, ISO/SAE 21434 incorporates Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) to evaluate cybersecurity risks in products. Effective cybersecurity risk assessment involves thoroughly examining the product to identify inherent risks. It is crucial to implement suitable measures to prevent these risks from being exploited by malicious actors. The severity of cybersecurity risks is evaluated based on four factors: threat scenario, damage scenario, attack path, and feasibility of executing the attack. The risk score derived from these factors informs decisions on how to address the risk effectively.
- Organizational clauses:
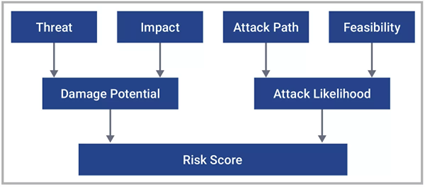
The threat scenario and its impact on the product assess the potential damage during its operational phase. Attack paths indicate how the threat might exploit vulnerabilities within the product. Feasibility measures how likely it is for the attack path to be successfully carried out. The combination of attack path and feasibility determines the likelihood of occurrence. The risk posed to the product is determined by combining the damage potential of the threat with the probability of its exploitation. A risk score is then calculated based on these four factors in combination.
UNECE R155 and ISO/SAE 21434
The UNECE R155 and ISO 21434 are both standards related to cybersecurity in the automotive industry
The UNECE R155 is a regulation developed by the World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations under the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). It specifically addresses cybersecurity and software updates for vehicles to establish requirements and guidelines to ensure the cybersecurity of vehicles throughout their lifecycle, including production, operation, and maintenance phases.
As a UNECE regulation, it is intended for adoption by member countries, which helps in creating a harmonized approach to cybersecurity standards in vehicles globally.
Relationship between UNECE R155 and ISO 21434:
Complementarity: While UNECE R155 is a regulation that sets mandatory requirements for vehicle cybersecurity, ISO 21434 is a standard that provides guidelines and best practices for cybersecurity engineering. In this sense, ISO 21434 can be used by manufacturers and suppliers to meet the requirements specified in UNECE R155.
Implementation: Manufacturers may choose to implement ISO 21434 to ensure compliance with the cybersecurity aspects of UNECE R155. ISO 21434 provides more detailed technical guidance and methodologies that can help in the practical implementation of cybersecurity measures across the vehicle lifecycle.
Global Perspective: UNECE R155 focuses on regulatory compliance within its member countries, while ISO 21434 has a broader international perspective and can be used globally by organizations in the automotive sector to enhance cybersecurity practices.
Basically, to sum up, the UNECE R155 and ISO 21434 are both crucial documents in the automotive cybersecurity landscape, with UNECE R155 providing regulatory requirements and ISO 21434 offering guidance for implementation. They are complementary in ensuring that vehicles are designed, produced, and maintained with robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber threats. Also, the ISO/SAE 21434 is an option to document the compliance of the UNECE R155.
LINK OF ISO/SAE 21434
