ISO/IEC 15408 Common Criteria
ISO/IEC 15408 Common Criteria refers to a global standardization for Information Technology (IT) products and systems security certification. ISO/IEC 15408 is also known as Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation, and often abbreviated as Common Criteria or CC.
What is its aim?
The primary objective of this standard is to provide a consistent set of standards for the security functionality of IT systems as well as the assurance procedures used to evaluate these products during security assessments. It gives buyers a measure to assess the security characteristics of IT products and enables sellers to have their goods independently assessed and certified to accepted security standards. [1], [2].

Scope and Structure
• The framework of ISO/IEC 15408 Commo Criteria comprises three main parts, as follows:
- Introduction and General Model: outlining the general concepts and basic framework for IT security evaluation.
- Security Functional Components: outlining the security functional requirements to be used as criteria during a product’s security evaluation.
- Security Assurance Components: defines in detail the criteria applied for assurance measures in evaluated products [3]
The standard introduces and encompasses a number of key components, upon which it largely relies for its implementation. These namely are: [4]
- Target of Evaluation (TOE), referring to the items (software, firmware, and/or hardware) that are the subjects considered to be evaluated for standardization.
- Protection Profile (PP), referring to a documentation template of security requirements for a specific class or range of related products. A Protection Profile is implementation-independent statement of security needs for a TOE.
- Security Target (ST), referring to the set of documented requirements that define the security properties of a specific product/service that is being evaluated. This is meant to allow vendors to customize evaluations to their given product’s capabilities. A Security Target is an implementation-dependent statement of security requirements for a given TOE, and can be viewed as a refinement of the above described PP.
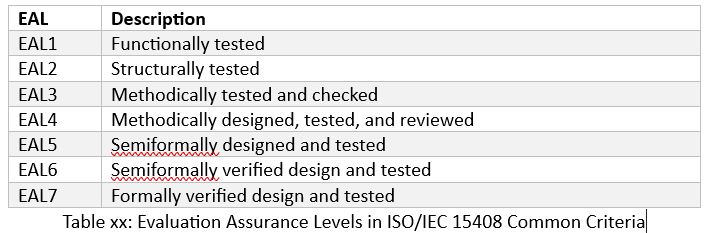
- Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL), referring to a numerical grading scale that indicates how thoroughly an IT product that follows the Common Criteria has been assessed. The EAL scale ranges from 1 to 7, with a higher value showing that a higher security assessment has been carried out, and therefore a higher degree of confidence can be had. Thus, the EAL is by no means a measure of the product’s security in its own right. The EAL’s seven distinct level and their significance are summarized in the table below
Audits for ISO/IEC 15408 Common Criteria are carried out in licensed facilities. The frequency of evaluations is largely driven by particular needs such as a changes or new features of a certified product, expiry of an existing certification, or the need to achieve a higher EAL.
A standard is customarily revised every five years and ISO/IEC 15408-5:2022, Common Criteria’s latest version, is currently at the stage of being revised. [5]
ISO/IEC 15408 Common Criteria is a standard that can be voluntarily implemented and has generic scope, potentially encompassing an entire range of industries such as government, defense, healthcare, finance, and telecommunications. However, it is evident that is of particular relevance to cases including critical infrastructures such products used in the EPES industry, where security is of paramount importance, and Common Criteria serves as a means of verification of claimed security attributes.
Lates updates on ISO/IEC 15408
In regard to ISO/IEC 15408 Common Criteria there have been no major recent developments registered. The current version is: 3.1, revision 5, with the latest part (ISO/IEC 15408-1:2022) published in August 2022. This is expected to be replaced by ISO/IEC DIS 15408-1 in the coming months
More information:
