What is ETIP SNET?
European Technology and Innovation Platform for Smart Networks for Energy Transition (ETIP SNET) serves as a collaborative forum within the European Union, bringing together experts from industry, academia, and the public sector to address issues related to smart grids, energy efficiency, and the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. The goal is to promote innovation and research in smart grid technologies to support the energy transition in Europe.
ETIP SNET key elements
Steering Committees: That oversees and coordinates its activities. This committee is composed of representatives from various stakeholders, including industry, academia, regulators, and government institutions.
Working Groups: ETIP SNET organizes thematic working groups to address specific areas of interest related to smart grids and the energy transition. These working groups bring together experts in their respective fields to research and develop solutions.
Public Consultations: The platform often conducts public consultations to gather opinions and inputs from a wide range of stakeholders. This helps ensure that decisions and recommendations are supported by the wider community.
Publications and Documents: ETIP SNET produces reports, guidelines, technical documents, and recommendations that reflect the current state of technology and research in the field of smart grids and the energy transition.
Events and Conferences: The platform organizes events, conferences, and workshops where experts can share knowledge, present research findings, and discuss challenges and opportunities in the field of smart grids.
Collaboration with External Organizations: ETIP SNET frequently collaborates with other organizations, institutions, and agencies related to energy and technology in Europe to promote innovation and the adoption of advanced solutions in the energy sector.

The main function of ETIP SNET is to promote research, innovation, and collaboration in the field of smart grids and energy transition in Europe. Some of the specific functions of ETIP SNET include: Strategy Development; Coordination of Research and Innovation; Generation of Recommendations and Guidelines; International Collaboration; Support for EU Energy Policy; Promotion of Cybersecurity and Network Resilience.
The resources available to achieve these functions are: Experts and Stakeholders;
Collaboration Network; Funding and Financial Resources; Data and Information; Communication Infrastructure; Policy Support; Influence Capacity.
To support Europe’s energy transition by guiding and identifying research and innovation R&I priorities addressing the innovation challenges for the energy system, ETIP SNET publishes and updates key documents that consolidate the views of more than 350 stakeholders.
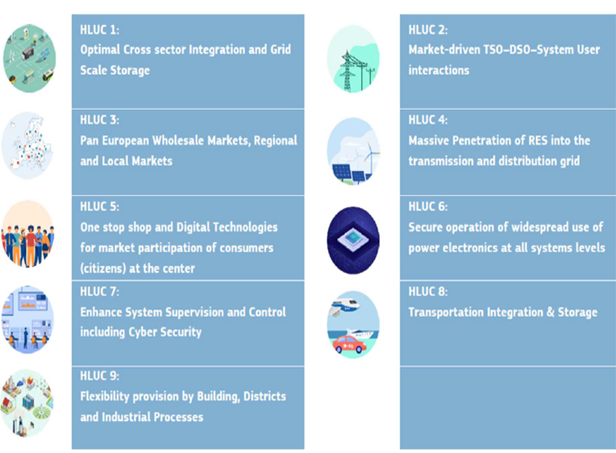
ETIP SNET use cases
The ETIP SNET proposed Project Priority Concepts based on the 9 High Level Use Cases (as defined in the ETIP SNET Roadmap 2022-2031) intending to underline the urgency of realising the transformation of today’s energy system through concrete R&I projects into the needed (partially) renewable energy system of 2031 and the fully CO2-neutral energy system of 2050 as the ultimate goal.
High Level Use Cases in the ETIP SNET Implementation Plan 2025 + including Cybersecurity:
Priority Project Concepts (PPCs), within HLUCs, are projects covering all integration features of the Future Energy Systems with concrete goals and time schedule.
The outcomes of the PPC should consider the current and the future Directives on cyber security.
It’s crucial to integrate cybersecurity into the energy system design, development, and operation, and to ensure that it is included as a critical factor in decision-making. This will enhance the resilience of the energy infrastructure, minimize the risk of cyber threats, and ensure the provision of secure and reliable energy services to consumers.
PPCs are expected to:
- Analyse the current and the future Directives on cybersecurity and consider all forms of energy networks: electricity, gas and hydrogen.
- Identify the specific ICT services, systems or products that might be subjected to coordinated risk assessments with priority, including risks in the renewable energy.
- Propose effective processes for crisis management to handle energy cybersecurity incidents involving more than one national stakeholder or stakeholders of cross-border relevance.
- Define training mechanisms for energy cybersecurity exercises to increase resilience and improve the risk preparedness of the energy sector.
- Implement and demonstrate a robust dynamic Cyber-Risk Evaluation methodology in order to detect threats and vulnerability of the targeted IT/OT environments in near real-time conditions and to propose corresponding mitigation actions.
- Establish minimum alerts and threat detection flows by setting up a system for the collection and sharing of essential information in relation to cyber incidents in the energy domain at EU level.
- Increase cyber situational awareness and improve response to cyberattacks by proposing a solid cooperation framework for cybersecurity aspects of cross-border energy flows in order to ensure the reliability of the energy systems and to ensure close collaboration with existing governance structure(s) for cybersecurity.
- Analyze the business models supporting the adoption of a cooperative energy cybersecurity framework at EU level.
- Determine a set of common criteria to perform risk assessments based on defined risk scenarios for the operational reliability of the energy systems with regard to cross-border flows and cascading attacks.
- Demonstrate energy sector’ cyber resilience to different attacks by exercising, simulation and real testing.
Latest updates on ETIP SNET
ETIP SNET updates in recent months:
- Ramp-up and role of hydrogen-based power generation (June 2024): This document provides guidelines and recommendations for the use of hydrogen in power generation to hydrogen in electric power generation to maintain a stable power supply with stable power supply with variable renewable energy sources.
- Energy Community Embedment Increasing Grid Flexibility and Flourishing Electricity Markets (May 2024): This paper discusses the role of energy communities for distribution system operators and distribution system operators and transmission system operators.
In addition, webinars are held that focus on the latest publications from the different Working Groups.
For more information about ETIP SNET´s features, objectives and organization can be found on its website https://smart-networks-energy-transition.ec.europa.eu/
